Access control consists of rules that you set to control the security of a Workbench project. You can set these rules at the project level or the directory (folder) level, and you can control who can access the parts of your data sets that are contained in cBases
By default, Workbench projects allow full access to administrative users and completely restrict access to non-administrative users. That is, all access control rules operate by providing access instead of restricting access, since all access for non-administrative users is restricted by default. You can grant non-administrative users permissions to access directories and portions of your data sets with the access control rules.
To enable access control in your project, see Managing Project Access.
NOTE:If a user does not have project access, access control rules do not apply to that user and the user's access is fully restricted.
Access rules fall into the following categories:
- File Access
- cBase Access
- Model Access
- DiveTab Access
- Audit Rules
Each rule is set either without or with a condition. Without a condition, the rule applies to all users. With a condition, the rule applies to a specified group, user, or property.
The condition types are:
- All Users—Applies to all users (default)
- Group—Applies to everyone within the named group
- User—Applies to the specific user
- Property—Applies to any user or group that has the specified property and value(s) pair
Opening the Access Control Tab
-
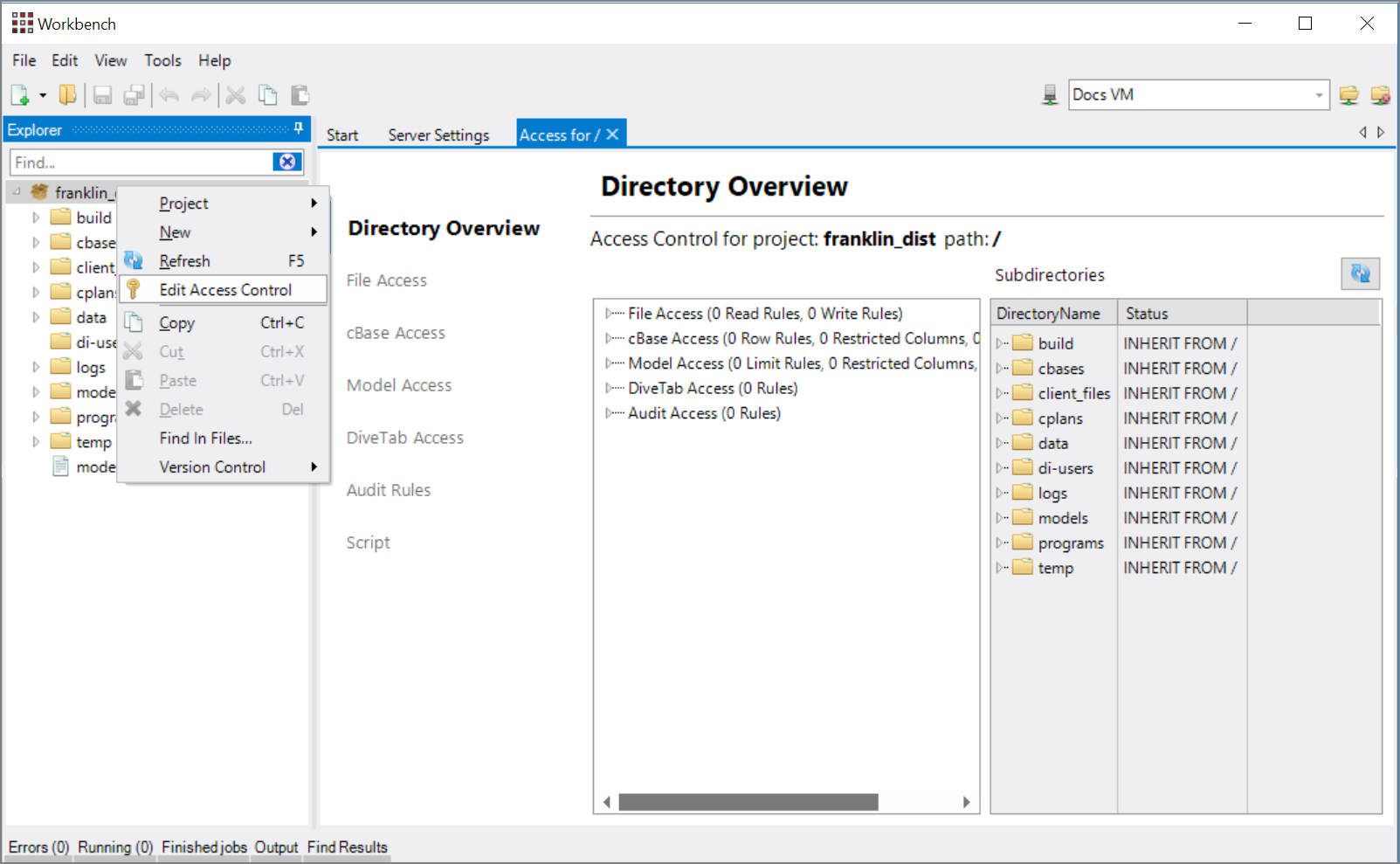
Right-click the project or folder in Workbench Explorer, and click Edit Access Control.
The Access for / tab opens. Note that the forward slash ("/") indicates that this is the project root. A directory name appears when opening from a folder, for example, Access for /cbases.
-
Click the appropriate sub-tab to set the access control rules that you need,
 as shown in this sample.
as shown in this sample.
NOTE:
-
The sub-tabs that are available vary with the installed DI license.
-
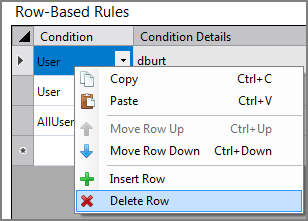
After rules are set in the rules tables, there are
 context-menu commands for editing the table rows.
context-menu commands for editing the table rows. -
Each new rule is set on a new row within the specific access sub-tab.
Inheritance:
Access control is either set on a project or directory, or it is not. This is true of all access control categories. If access control is not defined for a directory, then access control rules are inherited from the nearest ancestor that has any rules defined. It is not possible to inherit access for only one category. For instance, it is not possible to inherit file access control without also inheriting cBase access control. If no ancestor has access control defined, then the default, restrictive access is used.
NOTE:
- It is a best practice to set access rules at the project level and select the Inherit from ancestor check box for each folder in the project whenever possible.
- When access control is set on a project or directory, the underlying access script is saved in the project encoded in UTF-8.
- Access Control Lists
 access control list. The security tool that DiveLine 6.x uses to control user and group access to the server. DiveLine 7.x applies access control rules to projects and can apply ACLs to non-project resources that use the 6.4 DiveLine namespace. (ACLs) for 6.4 DiveLine Namespace and 6.4 Production Sandbox projects are maintained using the version 7.x DI-Config.
access control list. The security tool that DiveLine 6.x uses to control user and group access to the server. DiveLine 7.x applies access control rules to projects and can apply ACLs to non-project resources that use the 6.4 DiveLine namespace. (ACLs) for 6.4 DiveLine Namespace and 6.4 Production Sandbox projects are maintained using the version 7.x DI-Config.
If you are using Measure Factory, also see Factory Security.
See also:
- Access Control Interface
- Access Control Process
- Access Control Categories
- Directory Overview Tab
- Access Control Conditions
- Access Control Effects
- Configuring Access Control
- Properties Overview
Mentioned in: