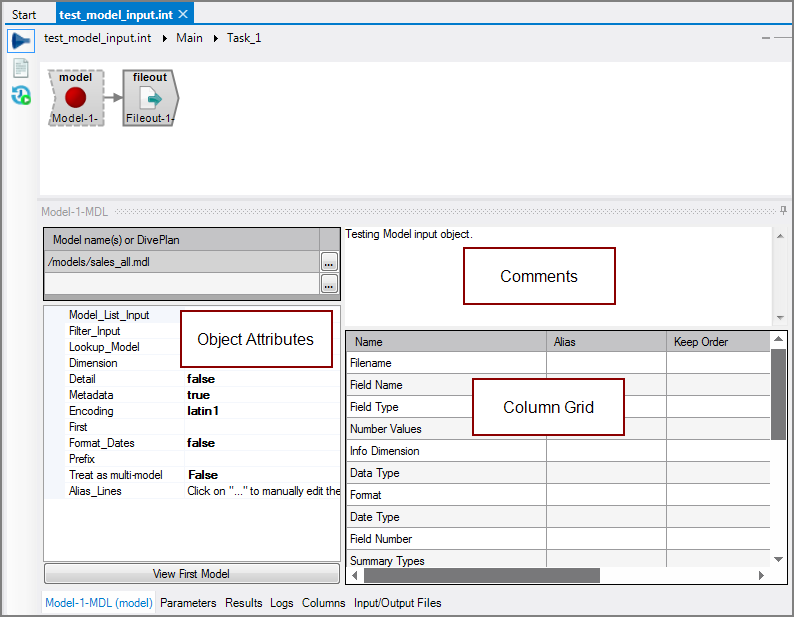
The Visual Integrator (VI) Model input object brings data into the script from a classic model.
![]()
The Model input object brings in standard model data as well as model metadata. If the model is a detail model, the detail fields can be brought into the output flow, including detail dimensions, detail summaries, and detail info fields.
The Model input object has ![]() three panes where you set attributes.
three panes where you set attributes.
You set attributes for the Model input object in the ![]() object attributes pane.
object attributes pane.
| Attribute | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
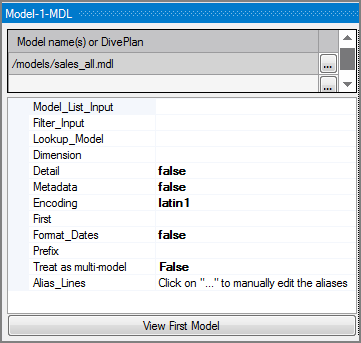
Model name(s) or DivePlan (required) |
Defines one or more input files as follows:
NOTE: At least one input file must be indicated. Do not use a Model name(s) or DivePlan attribute when using the Model_List_Input attribute because these attributes are mutually exclusive. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
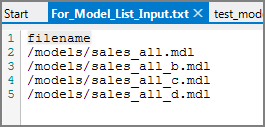
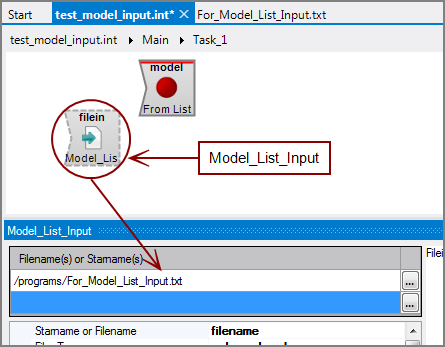
Model_List_Input |
Specifies a separate input flow object to generate a list of file names for the Model input object. This input flow object uses a single-column text file for input. The column name must be filename and the object must contain a This attribute allows programmatic control over the input. For example, this text file can be automatically generated from another VI script. The Model input object uses the values in the filename column as a list of files to open as its input. The input is formed by concatenating all files in the file list. Do not use a Model name(s) or DivePlan attribute when using the Model_List_Input attribute because these attributes are mutually exclusive.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Filter_Input |
Specifies a separate input flow containing filtered columns for a detail model. The input flow must specify the columns by checking the corresponding Filter check boxes in the Model input object's column grid. The values in the detail model that match the rows in this filter input flow are returned, providing fast access to the detail data based on the model dimensions. In effect, the detail model is used as an indexed file. This filtering method must be used against a single model, it does not support multi-models. To implement the Filter_Input attribute, you create a separate input object and connect it similar to the Model_List_Input attribute.
Do not use the Filter_Input attribute and the column grid Filter Values together because they are mutually exclusive. NOTE: Each input row of the filter flow is used to query the model for its combination of filter column values. If there are duplicate rows in the filter input for a set of filter column values, the same query runs again and these rows are returned out of the detail model multiple times. The order of the output rows corresponds to the order of filter values in the input flow. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lookup_Model |
Specifies a lookup model to use in a multi-model merge. Use only models specifically built as lookup models. The dimension values in the lookup model should exactly match the core dimension values of the regular model you are associating it with.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dimension |
Specifies one dimension or info field that appears in the output data flow. The output data flow becomes restricted to this one dimension and any associated info fields. When an info field is specified, a single column of the info field's values appear as a dynamic dimension in the output data flow. Dimension data returned this way is equivalent to a first-level dive on the dimension. All associated info fields are included. You can use the Keep and Remove check boxes in the column grid to control which info fields are included. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detail |
Specifies where to read data when using a detail model.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metadata |
Specifies if the Model input object passes metadata about the fields in the model or just the model data.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Encoding |
Defines how files names are read and interpreted in terms of character encoding. Values include:
UCS-2 and UTF-8 files can include a Byte Order Mark (BOM) at the beginning of the file to denote the file encoding. These file signatures are defined as follows:
File signatures are common for Unicode files on Windows operating systems. If the file input object reads multiple files, the signature of each file determines its encoding. If the encoding attribute is auto and no signature is found, the encoding is assumed to be latin1 if no other object in the task handles Unicode data and the VI file is not encoded as utf-8 (using the charset 1208 directive). Otherwise, the encoding is assumed to be utf-8. See also Integrator Unicode Data Support. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
First |
Specifies a number to limit how many records are read from each input file. This attribute is useful for script testing on a small number of records. If not used, all rows are read. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Format_Dates |
Specifies how date fields are passed in the output flow—string or numeric form.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Prefix |
Defines a prefix that is added to all column names in the flow. If you want a space between the prefix and the column name, include that space in the prefix string definition. Any columns assigned an alias do not use the prefix; instead, the columns use the alias name. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treat as multi-model |
Specifies whether the Model input object references multiple models or a single model. Does not apply to DivePlans.
NOTE: The attribute is automatically set to True when adding more than one model in the list of files. This attribute is not stored in the script, it cannot be modified by the user and is read only. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Alias_Lines |
Aliases can be set and edited in both the Alias_Lines attribute and the column grid. The column grid allows for graphical editing, while the Alias_Lines attribute is set at the code level in the following format: OldColumnName=NewColumnName For example: inv_nbr=Invoice Number Where Invoice Number is the alias for inv_nbr. The Alias_Lines method is useful for working with array parameters used as aliases. VI cannot process these array parameters because they are not in a format that VI can interpret. VI considers these array parameters to be malformed aliases and displays a warning message in the Logs tab. For example: Alias definition "$(ExternalAliases)" in object "From List" is not formatted as "OldColumn=NewColumn". When the line contains a parameter Integrator is most likely able to resolve it when the parameter is properly defined. To edit this alias definition use the "Alias_Lines" property. This message indicates that there is a malformed alias named $(ExternalAliases) in the object named From List. The array parameter displays as $(ExternalAliases) in the script. For VI to interpret this array parameter, you must assign an alias in the VI format.
|
Each object has an area where you can enter comments.
It is a DI best practice to enter a note for every object in a VI script. You can set a VI preference to give a warning for each object without a note.
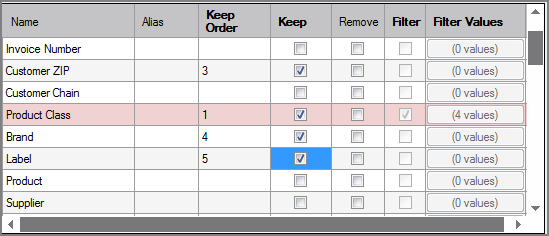
The ![]() Model Input column grid displays the columns from the input files.
Model Input column grid displays the columns from the input files.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Name |
Displays the name of each input column. This attribute is read-only. |
| Alias |
Defines alternate names for any of the input columns. Spaces before or after an alias column name are ignored. Spaces within an alias column name are acceptable. |
| Keep Order |
Manages the order that columns display in the output data flow. By default, columns that are passed to the next object in the data flow are displayed in the order that they appear in the Name column. You can change this order by typing a number in the Keep Order column. When you assign a Keep Order number, the Keep column is checked automatically. The Keep Order numbers might reorder to accommodate any changes you make. |
| Keep |
Manages which columns are kept in the output data flow. If no columns have a Keep check mark, all columns are kept in the output data flow, except for any explicitly marked Remove. Select the Keep check box for columns you want to explicitly keep in the output data flow. A number is automatically added in the Keep Order column when you select its Keep check box. After marking any column with a Keep check mark, only those marked Keep are kept in the output data flow. NOTE: After any Keep check boxes are checked, do not use the Remove check boxes as clicking a Remove check box sets all Keep check boxes to unchecked. |
| Remove |
Manages which columns are removed from the output data flow. Select the Remove check box for columns that you want to explicitly suppress from the output data flow. NOTE: Use the Remove check boxes only when no Keep check boxes are checked. |
| Filter | Filters data in a detail model based on the selected columns. These columns must appear in the input object specified by the Filter_Input attribute and be defined as dimensions in the model. Add a check mark to each input column that you want filtered. |
| Filter Values |
Provides an alternate method to filter data that is optimized for Tunnel parameters instead of using the Filter_Input attribute.
Do not use the Filter_Input attribute when using Filter Values because they are mutually exclusive. NOTE: Like the Filter_Input attribute, duplicate filter values cause duplicate rows to be returned from the model. |