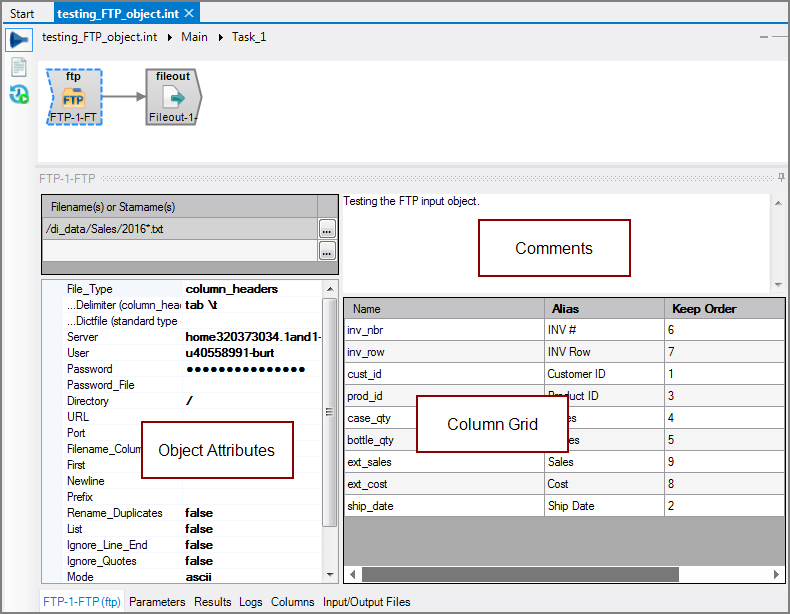
The Visual Integrator (VI) FTP input object reads data from an FTP server into the script.
![]()
FTP input object accepts input from one or more text files. The contents of the remote files are read directly into the data flow. Both systems must have the FTP protocol enabled. The text files are described by column headers within the file or by an external dictionary file.
The FTP object has ![]() three panes where you set attributes.
three panes where you set attributes.
You set attributes for the FTP object in the ![]() object attributes pane.
object attributes pane.
|
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Filename(s) or Starname(s) (required) |
For starname, you can use the wildcard characters question mark (?) or asterisk (*).
Wildcard character matching is case-insensitive and is limited to one directory only. To match in more than one directory, add additional rows to the section. TIP: If working with case sensitive file names, try using a Directory input object. You can filter on the filename metadata and feed it into a Filein object using the File_List_Input attribute. With the starname attribute, files are returned in the order that they are found in the directory; they are not necessarily sorted alphabetically. The order can vary across systems, and is often related to how files are deleted and added in the directory. Programs should not rely on the order of starnames. |
| File_Type |
Specifies how the columns are named in the input files. Choices are:
TIP: The file type ignore_column_headers allows you to use a dictionary with trim=false to keep leading spaces in the input data. |
|
Delimiter (required for column_headers file type) |
Specifies the delimiter that is used to separate columns for variable format files. If not specified, ASCII tab is used. Choices are:
|
|
Dictfile (standard type only) |
Specifies the file name for the dictionary that describes the columns. This attribute is used with legacy format dictionaries, which list both the column names and the data categories. Use the browse button to navigate to the dictionary file. |
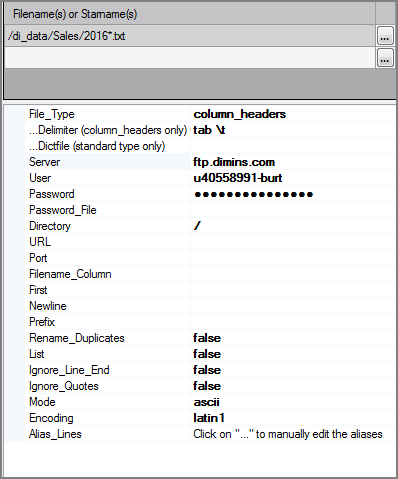
| Server |
Specifies the hostname or IP address for the FTP server. Any IPv6 addresses are automatically converted to IPv4 addresses. The Server and URL attributes are mutually exclusive—specify one or the other. |
| User | Specifies the logon username for the FTP server. Conflicts with the URL attribute if the URL includes the username. |
| Password |
Specifies the logon password for the FTP server. If not specified, no password is required when logging into an FTP server. Conflicts with the URL attribute if the URL includes the password. The Password and Password_File attributes are mutually exclusive—use one or the other. |
| Password_File |
Specifies a file containing the logon password for the FTP server. The password must be on the first line in the file. This allows you to store the password outside the VI script. The Password and Password_File attributes are mutually exclusive—use one or the other. |
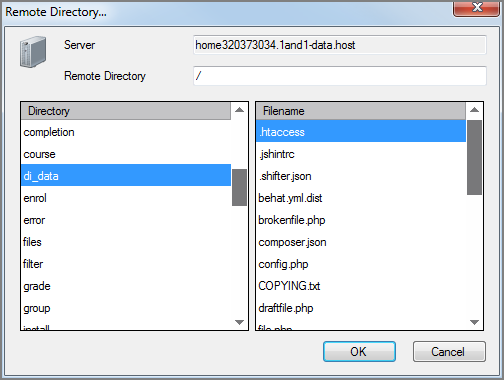
| Directory |
Specifies the remote directory on the FTP server for the input files. Conflicts with the URL attribute; do not use both the Directory and URL attributes.
|
| URL |
Specifies the FTP server and file name in URL format. The URL must begin with ftp and have the general format of: ftp://<server>/<filename> The file name can use wildcard characters as described in the Filename(s) or Starname(s) attribute. Optionally, you can define the User, Password, and Port attributes in the URL attribute by using the following format: ftp://<user>:<password>@<server>:<port_number>/<filename> The URL attribute can conflict with several other attributes, so use caution.
|
| Port | Specifies the port for the FTP server. The default value is 21, which is the Internet standard port for FTP. Do not use the Port attribute if using the URL attribute. |
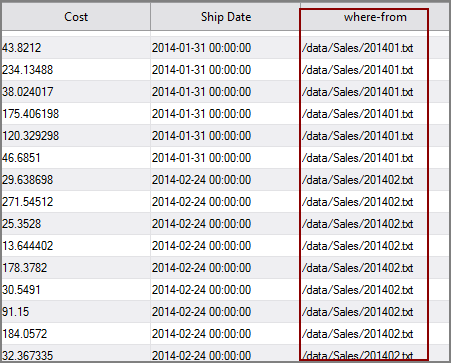
| Filename_Column |
Specifies a name for a new column added to the output flow for example, where-from. The values in this column contain the path and file name indicating where each input row of data originated as shown in the example output This attribute is useful for troubleshooting when using multiple input files. |
| First |
Specifies a number to limit how many records are read from each input file. This attribute is useful for script testing on a small number of records. If not used, all rows are read. |
| Newline |
Specifies a newline character as a string containing exactly one character from the input file. The newline character is replaced with a line break. For example: With ~ set as the newline character: 483574387548~4434839~4782939029~ becomes in the output flow: 483574387548 4434839 4782939029
If not specified, the default newline character is a carriage return (ASCII 13), a line feed (ASCII 10), or a carriage return line feed. |
| Prefix | Defines a prefix that is added to all column names in the flow. If you want a space between the prefix and the column name, include that space in the prefix string definition. Any columns assigned an alias do not use the prefix; instead, the columns use the alias name. |
| Rename_Duplicates |
Renames duplicate columns so that each column in the output data flow has a unique name. The duplicate naming process occurs before attributes defining aliases, prefixes, or the columns to keep are applied, so these generated column names can be aliases to another name.
|
| List |
Controls whether the FTP input object returns a list of files or the contents of the named files.
|
| Ignore_Line_End |
Specifies whether or not parse errors dealing with the end of an input line are ignored. For example, Fixed field occurs past end of line or Too few fields. This attribute helps control processing when there are too few data items in an input row.
|
| Ignore_Quotes |
Specifies whether or not the beginning and ending quotation marks are ignored while keeping embedded quotes. This optional attribute is intended to be used in special cases only.
|
|
Mode |
Defines whether the data is transferred in ascii or binary mode.
|
| Encoding |
Defines how files names are read and interpreted in terms of character encoding. Values include:
UCS-2 and UTF-8 files can include a Byte Order Mark (BOM) at the beginning of the file to denote the file encoding. These file signatures are defined as follows:
File signatures are common for Unicode files on Windows operating systems. If the file input object reads multiple files, the signature of each file determines its encoding. If the encoding attribute is auto and no signature is found, the encoding is assumed to be latin1 if no other object in the task handles Unicode data and the VI file is not encoded as utf-8 (using the charset 1208 directive). Otherwise, the encoding is assumed to be utf-8. See also Integrator Unicode Data Support. |
| Alias_Lines |
Aliases can be set and edited in both the Alias_Lines attribute and the column grid. The column grid allows for graphical editing, while the Alias_Lines attribute is set at the code level in the following format: OldColumnName=NewColumnName For example: inv_nbr=Invoice Number Where Invoice Number is the alias for inv_nbr. The Alias_Lines method is useful for working with array parameters used as aliases. VI cannot process these array parameters because they are not in a format that VI can interpret. VI considers these array parameters to be malformed aliases and displays a warning message in the Logs tab. For example: Alias definition "$(ExternalAliases)" in object "From List" is not formatted as "OldColumn=NewColumn". When the line contains a parameter Integrator is most likely able to resolve it when the parameter is properly defined. To edit this alias definition use the "Alias_Lines" property. This message indicates that there is a malformed alias named $(ExternalAliases) in the object named From List. The array parameter displays as $(ExternalAliases) in the script. For VI to interpret this array parameter, you must assign an alias in the VI format.
|
Each object has an area where you can enter comments.
It is a DI best practice to enter a note for every object in a VI script. You can set a VI preference to give a warning for each object without a note.
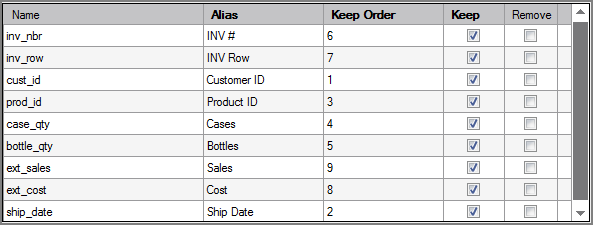
The ![]() FTP column grid allows you to choose which metadata to include in the output data flow.
FTP column grid allows you to choose which metadata to include in the output data flow.
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| Name | Displays the name of each input column. This attribute is read-only. |
| Alias | Defines alternate names for any of the input columns. Spaces before or after an alias column name are ignored. Spaces within an alias column name are acceptable. |
| Keep Order | Manages the order that columns display in the output data flow. By default, columns that are passed to the next object in the data flow are displayed in the order that they appear in the Name column. You can change this order by typing a number in the Keep Order column. When you assign a Keep Order number, the Keep column is checked automatically. The Keep Order numbers might reorder to accommodate any changes you make. |
| Keep |
Manages which columns are kept in the output data flow. If no columns have a Keep check mark, all columns are kept in the output data flow, except for any explicitly marked Remove. Select the Keep check box for columns you want to explicitly keep in the output data flow. A number is automatically added in the Keep Order column when you select its Keep check box. After marking any column with a Keep check mark, only those marked Keep are kept in the output data flow. NOTE: After any Keep check boxes are checked, do not use the Remove check boxes as clicking a Remove check box sets all Keep check boxes to unchecked. |
| Remove |
Manages which columns are removed from the output data flow. Select the Remove check box for columns that you want to explicitly suppress from the output data flow. NOTE: Use the Remove check boxes only when no Keep check boxes are checked. |